In 2025, architecture in India is undergoing a significant transformation, driven by the urgent
need to balance rapid urban development with environmental responsibility. Larger cities
continue to expand at a faster pace than mid-sized towns, putting immense pressure on
available resources and infrastructure. As a response, architects across the country are
focusing on sustainable practices—incorporating eco-conscious design elements, choosing
environment-friendly materials, and embracing traditional craftsmanship to create buildings that
are both modern and mindful of their ecological footprint.
Sustainable architecture is no longer just a theoretical aspiration; it has become a practical
and
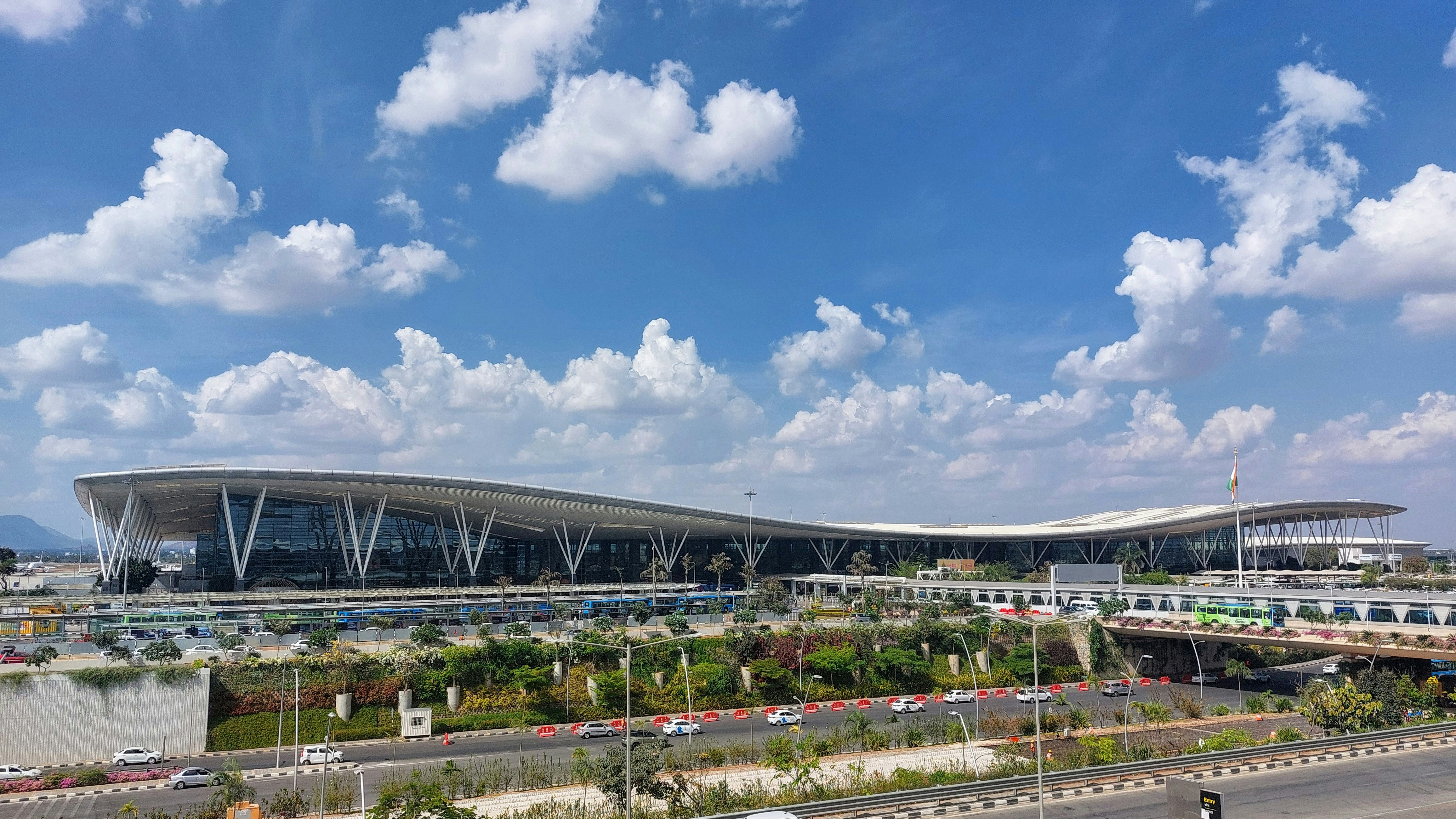
necessary reality. A shining example of this shift is the new Terminal 2 at Kempegowda
International Airport in Bengaluru. Designed as a “Terminal in a Garden,” it
integrates nature
into its very structure. The terminal features an expansive indoor forest belt, extensive use of
natural materials like bamboo, and green systems such as rainwater harvesting and
energy-efficient technology. It stands as a testament to how public infrastructure can embrace
sustainability without compromising on functionality or aesthetics.

Beyond airports and public spaces, the use of local and natural materials is gaining
popularity
across residential and commercial projects. Materials like mud bricks, lime plaster,
rammed
earth, and reclaimed wood are making a comeback, not only for their low
environmental impact
but also for their role in preserving India’s rich heritage of construction
techniques. In many
regions, architects are consciously incorporating local art and craft traditions
into their designs,
helping sustain livelihoods while promoting cultural continuity.
At the same time, technological advancements are shaping the way buildings are
designed and
operated. In 2025, smart architecture is on the rise. Artificial intelligence and
IoT (Internet of
Things) are being used to optimize energy use, automate systems like lighting and
ventilation,
and create buildings that respond intelligently to their environment. Predictive
maintenance,
real-time energy monitoring, and even AI-generated design solutions are making
buildings more
efficient, adaptable, and cost-effective over time.
Urban spaces are also being reimagined to tackle the constraints of land and the
need for
greenery. Vertical gardens, green walls, and rooftop farms are transforming how
urban buildings
contribute to the environment. These innovations not only improve air quality and
reduce heat
but also offer a sense of calm and beauty amidst the concrete sprawl. In cities like
Mumbai and
Delhi, high-rises and public buildings now incorporate these features as standard
rather than
exception.

Another key development is the rise of circular economy principles in construction.
Architects
are increasingly designing buildings with modular components and recyclable
materials,
enabling easier repair, adaptation, and eventual disassembly. This approach
minimizes
construction waste and extends the life cycle of buildings, making them more
sustainable from
conception to demolition.
India's green building market is indeed projected to reach USD 39 billion by 2025.
This
projection is supported by a joint report from Resurgent India and NAREDCO, which
highlights
that the commercial segment is expected to generate USD 11 billion, while the
residential
segment is projected to reach USD 28 billion, together totaling USD 39 billion by
2025.
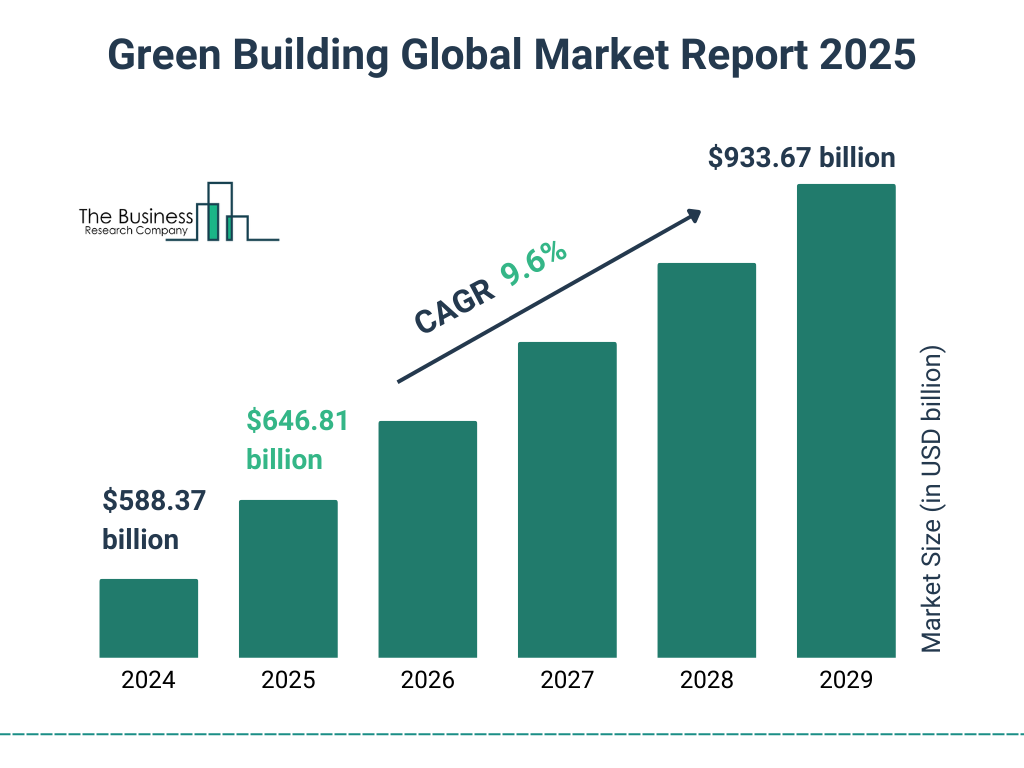
Source: https://www.thebusinessresearchcompany.com/report/green-building-global-market-report
Additionally, the global green building market is anticipated to experience
significant growth.
While specific figures for 2027 vary, the sector is expected to expand
substantially, driven by
increasing environmental awareness, technological advancements, and supportive
policies
worldwide.
In India, government policies and incentives play a crucial role in encouraging this
green
transition. The Energy Conservation Building Code (ECBC), along with certification
systems like
IGBC and GRIHA, are laying the foundation for responsible construction. These
initiatives
promote energy efficiency, sustainable building practices, and the use of
eco-friendly materials,
aligning with global sustainability goals.
In summary, the momentum toward eco-friendly architecture is undeniable, with both
national
and global markets showing significant growth prospects, supported by robust
government
policies and increasing public awareness.
However, challenges remain. High upfront costs, limited public awareness, and a
shortage of
trained green building professionals continue to slow down adoption. Yet, through
collaborative
efforts between the government, private sector, and educational institutions, these
barriers are
being addressed gradually. The focus is not only on constructing better buildings
but also on
fostering a more informed, skilled, and environmentally-conscious society.
As India strides into a greener tomorrow, eco-friendly architecture is emerging as a
cornerstone
of sustainable development. It showcases how economic growth and environmental
responsibility can go hand in hand. The country’s commitment to sustainable design
sets a
powerful example for other developing nations, proving that a future rooted in
tradition,
supported by technology, and driven by sustainability is not only possible—but
already in
motion.
Ready to build sustainably?
If
you
are
looking
for
sustainable
architectural
solutions
in Patna, Bihar or Jharkhand, or want to
collaborate on eco-conscious residential or commercial design,
Creative Designers brings
over 30 years of expertise in blending innovation
with
tradition. Reach out to us for architectural consultation, interior design, or green
building
planning.
Use our Architecture Cost Calculator to estimate your project budget—tailored for green
building materials, smart design features, and eco-conscious planning.
Try the Cost Calculator Now
.png)
.png)

